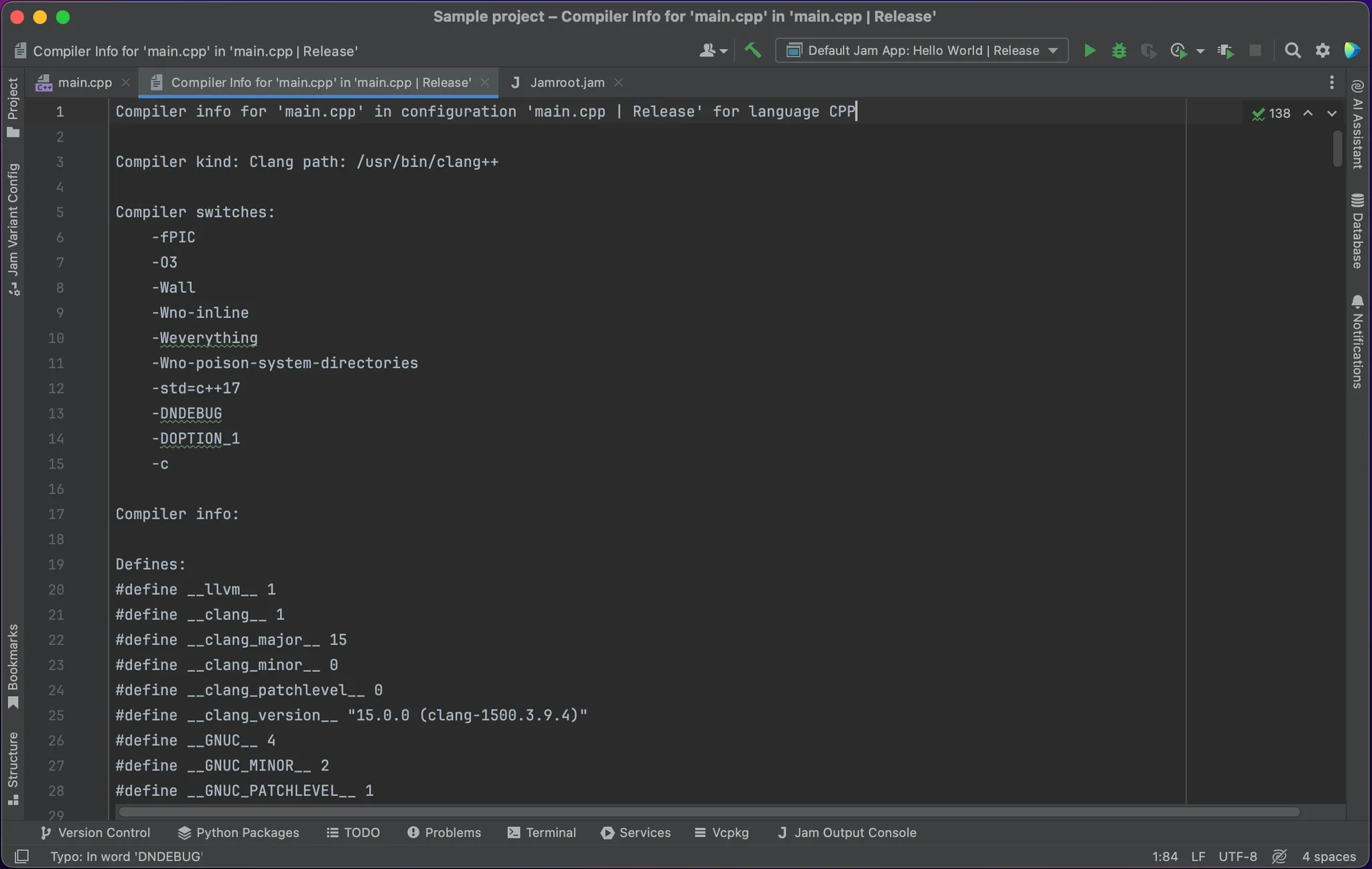
Guide to the Command Parser
What is the purpose of the command parser?
The command parser reads the output of Jam and parses the build commands found in it. It runs when the workspace is reloaded.
Example Jam Output
b2 -t hello_world release toolset=clang define=OPTION_1 -n -a
...found 8 targets...
...updating 3 targets...
common.mkdir bin/clang-darwin-15/release
mkdir -p "bin/clang-darwin-15/release"
clang-darwin.compile.c++ bin/clang-darwin-15/release/main.o
"clang++" -fPIC -O3 -Wall -Wno-inline -Weverything -Wno-poison-system-directories -std=c++17 -DNDEBUG -DOPTION_1 -c -o "bin/clang-darwin-15/release/main.o" "main.cpp"
clang-darwin.link bin/clang-darwin-15/release/hello_world
"clang++" -o "bin/clang-darwin-15/release/hello_world" "bin/clang-darwin-15/release/main.o" -fPIC
...updated 3 targets...
Done
Example Results
How to Configure It?
Go to Settings -> Build, Execution, Deployment -> Jam -> Build Command Parser.
The default configuration (as shown in the image) works well in most cases.
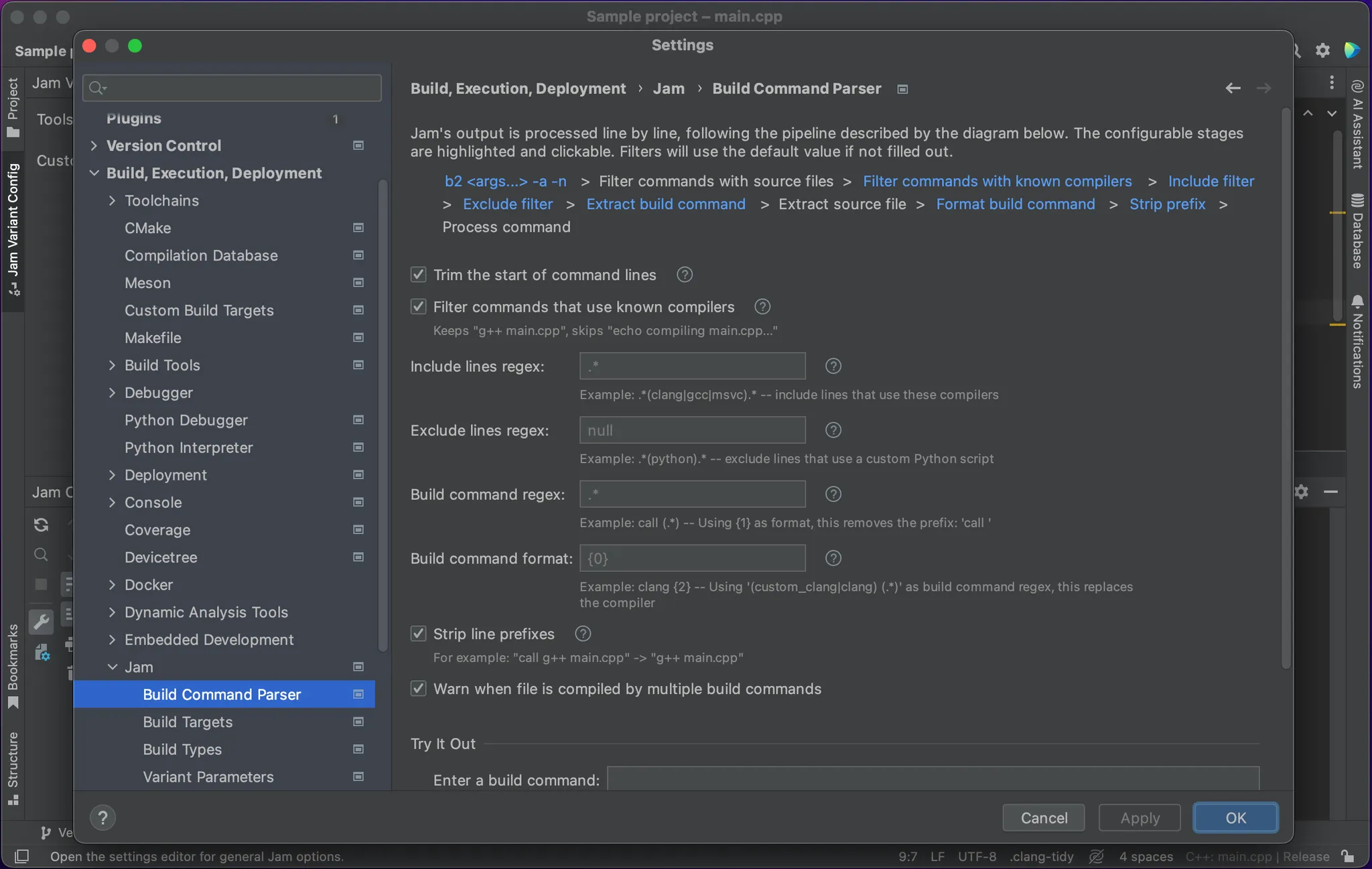
The Pipeline
The console output goes through a pipeline until you get the final build commands. The parser processes the output line-by-line.
Let's use an example to demonstrate how the parser works:
Input of the example used in the following sections
b2 -t hello_world release toolset=clang define=OPTION_1 -n -a
...found 8 targets...
...updating 3 targets...
common.mkdir bin/clang-darwin-15/release
mkdir -p "bin/clang-darwin-15/release"
clang-darwin.compile.c++ bin/clang-darwin-15/release/main.o
"echo" compiling main.cpp
python generate_stuff.py -o bin/clang main.cpp
call "clang++" -fPIC -O3 -Wall -Wno-inline -Weverything -Wno-poison-system-directories -std=c++17 -DNDEBUG -DOPTION_1 -c -o "bin/clang-darwin-15/release/main.o" "main.cpp"
clang-darwin.compile.c++ bin/clang-darwin-15/release/source file.o
"echo" compiling source file.cpp
python generate_stuff.py -o bin/clang "source file.cpp"
call "clang++" -fPIC -O3 -Wall -Wno-inline -Weverything -Wno-poison-system-directories -std=c++17 -DNDEBUG -DOPTION_1 -c -o "bin/clang-darwin-15/release/source file.o" "source file.cpp"
clang-darwin.compile.c++ bin/clang-darwin-15/release/dont_care.o
"echo" compiling dont_care.cpp
python generate_stuff.py -o bin/clang dont_care.cpp
call "clang++" -fPIC -O3 -Wall -Wno-inline -Weverything -Wno-poison-system-directories -std=c++17 -DNDEBUG -DOPTION_1 -c -o "bin/clang-darwin-15/release/dont_care.o" "dont_care.cpp"
clang-darwin.link bin/clang-darwin-15/release/hello_world
"clang++" -o "bin/clang-darwin-15/release/hello_world" "bin/clang-darwin-15/release/main.o" -fPIC
...updated 3 targets...
DoneNotes:
- The input contains commands that use
echoorpython, but still use the source files in their command line arguments. The parser needs to discard these lines. - The compiler is not called directly, it's invoked through the
callcommand. The parser needs to extract the compiler invocation. - There is a source file with a whitespace in its name. The parser needs to correctly parse it as a single command line argument: source file.cpp.
- Let's also replace the compiler with
gccjust for the sake of demonstration. - In addition, let's discard the build command for dont_care.cpp, again, for the sake of demonstration.
Trimming the leading whitespaces
Whitespaces are optionally removed from the beginning of each line. This helps with the regular expressions later.
- Options:
- Trim the start of command lines: enable/disable
Result:
b2 -t hello_world release toolset=clang define=OPTION_1 -n -a
...found 8 targets...
...updating 3 targets...
common.mkdir bin/clang-darwin-15/release
mkdir -p "bin/clang-darwin-15/release"
clang-darwin.compile.c++ bin/clang-darwin-15/release/main.o
"echo" compiling main.cpp
python generate_stuff.py -o bin/clang main.cpp
call "clang++" -fPIC -O3 -Wall -Wno-inline -Weverything -Wno-poison-system-directories -std=c++17 -DNDEBUG -DOPTION_1 -c -o "bin/clang-darwin-15/release/main.o" "main.cpp"
clang-darwin.compile.c++ bin/clang-darwin-15/release/source file.o
"echo" compiling source file.cpp
python generate_stuff.py -o bin/clang "source file.cpp"
call "clang++" -fPIC -O3 -Wall -Wno-inline -Weverything -Wno-poison-system-directories -std=c++17 -DNDEBUG -DOPTION_1 -c -o "bin/clang-darwin-15/release/source file.o" "source file.cpp"
clang-darwin.compile.c++ bin/clang-darwin-15/release/dont_care.o
"echo" compiling dont_care.cpp
python generate_stuff.py -o bin/clang dont_care.cpp
call "clang++" -fPIC -O3 -Wall -Wno-inline -Weverything -Wno-poison-system-directories -std=c++17 -DNDEBUG -DOPTION_1 -c -o "bin/clang-darwin-15/release/dont_care.o" "dont_care.cpp"
clang-darwin.link bin/clang-darwin-15/release/hello_world
"clang++" -o "bin/clang-darwin-15/release/hello_world" "bin/clang-darwin-15/release/main.o" -fPIC
...updated 3 targets...
DoneFiltering commands with source files
Lines are automatically removed that don't contain anything resembling a source file: a string ending in .cpp or any other valid C++ source file extension.
This step is not configurable.
Result:
"echo" compiling main.cpp
python generate_stuff.py -o bin/clang main.cpp
call "clang++" -fPIC -O3 -Wall -Wno-inline -Weverything -Wno-poison-system-directories -std=c++17 -DNDEBUG -DOPTION_1 -c -o "bin/clang-darwin-15/release/main.o" "main.cpp"
"echo" compiling source file.cpp
python generate_stuff.py -o bin/clang "source file.cpp"
call "clang++" -fPIC -O3 -Wall -Wno-inline -Weverything -Wno-poison-system-directories -std=c++17 -DNDEBUG -DOPTION_1 -c -o "bin/clang-darwin-15/release/source file.o" "source file.cpp"
"echo" compiling dont_care.cpp
python generate_stuff.py -o bin/clang dont_care.cpp
call "clang++" -fPIC -O3 -Wall -Wno-inline -Weverything -Wno-poison-system-directories -std=c++17 -DNDEBUG -DOPTION_1 -c -o "bin/clang-darwin-15/release/dont_care.o" "dont_care.cpp"Filtering commands with known compilers
Lines are discarded if they don't contain anything resembling a compiler. Compilers are identified by their standard commands (clang, gcc, etc.). The plugin includes a predefined set of known compilers.
This filter also accepts the compiler specified in the toolchain.
- Options:
- Enable/disable: Filter commands that use known compilers
- Known compilers: Specify your custom compiler in the toolchain. This filter will accept it.
Result:
python generate_stuff.py -o bin/clang main.cpp
call "clang++" -fPIC -O3 -Wall -Wno-inline -Weverything -Wno-poison-system-directories -std=c++17 -DNDEBUG -DOPTION_1 -c -o "bin/clang-darwin-15/release/main.o" "main.cpp"
python generate_stuff.py -o bin/clang "source file.cpp"
call "clang++" -fPIC -O3 -Wall -Wno-inline -Weverything -Wno-poison-system-directories -std=c++17 -DNDEBUG -DOPTION_1 -c -o "bin/clang-darwin-15/release/source file.o" "source file.cpp"
python generate_stuff.py -o bin/clang dont_care.cpp
call "clang++" -fPIC -O3 -Wall -Wno-inline -Weverything -Wno-poison-system-directories -std=c++17 -DNDEBUG -DOPTION_1 -c -o "bin/clang-darwin-15/release/dont_care.o" "dont_care.cpp"Note:
This stage didn't discard the commands that use python because "bin/clang" looks like a compiler invocation.
Include filter
This is a regular expression that discards lines that don't match it.
- Options for Include lines regex:
- Empty text: No filter used
- A valid regular expression: It will be used as a filter
Results:
Include lines regex: .*(main|source file)\.cpp.*
python generate_stuff.py -o bin/clang main.cpp
call "clang++" -fPIC -O3 -Wall -Wno-inline -Weverything -Wno-poison-system-directories -std=c++17 -DNDEBUG -DOPTION_1 -c -o "bin/clang-darwin-15/release/main.o" "main.cpp"
python generate_stuff.py -o bin/clang "source file.cpp"
call "clang++" -fPIC -O3 -Wall -Wno-inline -Weverything -Wno-poison-system-directories -std=c++17 -DNDEBUG -DOPTION_1 -c -o "bin/clang-darwin-15/release/source file.o" "source file.cpp"Exclude filter
This is a regular expression that discards lines that match it.
- Options for Exclude lines regex:
- Empty text: No filter used
- A valid regular expression: It will be used as a filter
Results:
Exclude lines regex: .*generate_stuff\.py.*
call "clang++" -fPIC -O3 -Wall -Wno-inline -Weverything -Wno-poison-system-directories -std=c++17 -DNDEBUG -DOPTION_1 -c -o "bin/clang-darwin-15/release/main.o" "main.cpp"
call "clang++" -fPIC -O3 -Wall -Wno-inline -Weverything -Wno-poison-system-directories -std=c++17 -DNDEBUG -DOPTION_1 -c -o "bin/clang-darwin-15/release/source file.o" "source file.cpp"Format build command
This step optionally transforms lines using a regular expression and a format string.
Although this step also uses a regular expression, it is not used for filtering.
It is still used for validation, though: Any lines that get this far have to match this regular expression (if specified).
- Options:
- Build command regex: Specify a valid regular expression to enable formatting, or leave it empty to keep the line as is.
- Build command format: Enter a string that can use regex match groups from the build command regex.
Build Command Format:
It's a string, where substrings in the format {n} are substituted with the nth match group from the build command regex. The index n has to be a valid match group.
Examples:
- This will turn
'call g++ main.cpp'into'g++ main.cpp': - Build command regex:
call (.*) - Build command format:
{1}
- This will turn
'clang main.cpp'into'gcc main.cpp': - Build command regex:
(clang) (.*) - Build command format:
gcc {2}
Result:
Build command regex: (.*)(clang\+\+)(.*)
Build command format: {1}gcc{3}
call "gcc" -fPIC -O3 -Wall -Wno-inline -Weverything -Wno-poison-system-directories -std=c++17 -DNDEBUG -DOPTION_1 -c -o "bin/clang-darwin-15/release/main.o" "main.cpp"
call "gcc" -fPIC -O3 -Wall -Wno-inline -Weverything -Wno-poison-system-directories -std=c++17 -DNDEBUG -DOPTION_1 -c -o "bin/clang-darwin-15/release/source file.o" "source file.cpp"Notes:
This example replaces the compiler based on a regex.
Split to command line arguments
The lines should be valid shell commands by now.
This step will split the lines into lists of command line arguments. It relies on the selected toolchain to know the syntax of the current shell: Bash shell, Windows shell, etc.
- Options:
- Select the right toolchain in Settings -> Build, Execution, Deployment -> Jam: This defines the syntax of the lines.
Result:
Strip compiler prefix
This stage receives a list of command line arguments, as processed by the previous step.
This will remove command line arguments that precede the compiler itself.
This is useful if the compiler is not called directly by Jam, but rather through another command.
- Examples:
'call gcc main.cpp'->'gcc main.cpp'
- Options:
- Enable/disable: Strip line prefixes
Result:
Extract the source file
The source file is extracted from the command line argument list, based on its file extension (.cpp or other known C++ source extensions).
Commands are discarded that don't contain any recognizable source files.
Nothing to be configured here.
Result:
Processing the command
This stage generates the so-called resolve configuration for the source files.
Most of this is handled by CLion and cannot be configured.